Lithium-ion batteries are considered new, but have long been ubiquitous in our lives. Due to the impact of electric vehicles and the energy crisis, lithium-ion batteries have become one of the most talked-about and confusing topics today. Compared to lead-acid batteries, which have been used in the industry for a long time and have not had many alternatives so far, by what criteria should one invest and switch to lithium-ion batteries with higher technology? Innovation is a very confusing question.
First of all, not everyone is a lithium battery customer. There is no rule that says everyone will use lithium batteries. If the application/operation removes lead-acid batteries and the user is satisfied, there is no need to invest in lithium batteries. The golden rule is to understand the customer's needs, analyze their operations, and ask the right questions. After these answers, it can only be said whether lithium batteries are needed.
Below we explore 5 questions and criteria for switching to lithium batteries:
• Will the existing lead-acid batteries last a full work shift without any issues and requiring battery replacement?
• Will the lead-acid batteries charge each other due to the intensity of the operation?
• Is battery maintenance an issue for the business? Is regular maintenance adequately performed?
• Are there any violations or adverse situations regarding safety and occupational health and safety?
• How important is energy efficiency?
• Is the service life of the lead-acid batteries sufficient?
Battery Replacement/Backup Battery Issues
When using lithium batteries, it is generally not necessary to replace batteries or keep backup batteries. A lithium battery of the same capacity; it runs on average about 25% longer than a lead-acid battery, allowing equipment to run longer. This advantage, combined with the benefits of fast and intermediate charging, allows businesses with three shifts to take advantage of the time lost to replacing batteries without having to keep backup batteries. You can reduce business cost items by eliminating or minimizing the cost of backup batteries. In addition, the battery charging area and backup battery area vacated after the transition to lithium batteries can be used for different purposes, perhaps making a storage area. Charging lithium batteries does not require special ventilation rooms or other requirements.
Battery Maintenance
One of the important reasons to switch to lithium-ion batteries is battery maintenance, which is both time-consuming and costly. If there are not enough maintenance personnel on site or the operator does not replenish the pure water of the lead-acid battery in time, the battery will soon be exhausted. These maintenance are basically;
• Checking electrolyte levels,
• Corrosion cleaning,
• Adding pure water,
• Regular battery balancing,
Regular maintenance is very important for the long-term effective use of lead-acid batteries. If the company does not have enough personnel for maintenance or wants to completely eliminate maintenance costs, these advantages can be provided by switching to lithium batteries.
Charging issues with lead-acid batteries
Lithium batteries can be fully charged in just 2 hours with fast charging. Considering that it takes about 8 hours to fully charge a lead-acid battery, a 2-hour charge means that the battery can be charged 4 times faster on average.
Examining the fast charging issues in two different lead-acid usage scenarios will be more helpful to understand whether this advantage is needed;
In the first scenario, we assume that the business does not have a spare battery. Lead-acid batteries; just put the vehicle on the charger to charge. It takes about 10 hours for the battery to cool, charge and rest after charging. This means that the vehicle is not used and idle for more than 1 shift.
Scenario two, assuming that the business has a spare battery, this time the stacker/forklift with a dead battery goes to the replacement station to replace the battery, the vehicle is not in a charging state, and most of the time it is replaced with a spare battery that is not fully charged. The disadvantage here is the cost of the spare battery, and therefore the increased maintenance cost... 20 minutes per shift. 1 hour of time is wasted every day due to battery replacement and possible work-related accidents when replacing the battery.
In companies using lithium batteries, intermediate charging is usually done by charging the machine during meal times, coffee breaks and idle time, without the need to purchase spare batteries. Combined with the advantages of fast charging, it can run continuously for 24 hours.
Energy Costs
Lithium batteries; offer about 30% higher energy efficiency in terms of storing energy from the grid and converting the stored energy into work without loss (when used with a high-frequency charger) compared to lead-acid batteries. This efficiency is directly related to the coulombic efficiency of lithium batteries of over 99%, which we reviewed earlier in our article on battery system efficiency. The equivalent of this efficiency in the field is: you can manage your operations with fewer lithium battery charges than lead-acid batteries, thus reducing your electricity bill. If a business has efficiency-enhancing activities and sustainability goals, then the transition to lithium batteries will be inevitable, even if not now.
Occupational Health and Safety Issues
Switching to lithium batteries completely protects against the following basic threats and hazards;
• Acid spills/overflows
• Overcharging/overheating
• Toxic and explosive gas fumes
• Workplace accidents when changing batteries
In lithium batteries, a control card called a BMS protects the entire structure. The battery and the operator are protected by overcharge/discharge, high temperature and current protection. Lithium batteries made with lithium iron phosphate chemistry are just as dangerous as lead-acid batteries. In the worst case, the battery reaches activation temperature (250C-300C) and starts releasing smoke. Due to the chemistry, the cells do not contain oxygen, so there is no risk of flame or fire like with NMC chemistry. Cooling with water is sufficient.
 Ganfeng Lithium Battery Passed the Short circuit test
Ganfeng Lithium Battery Passed the Short circuit test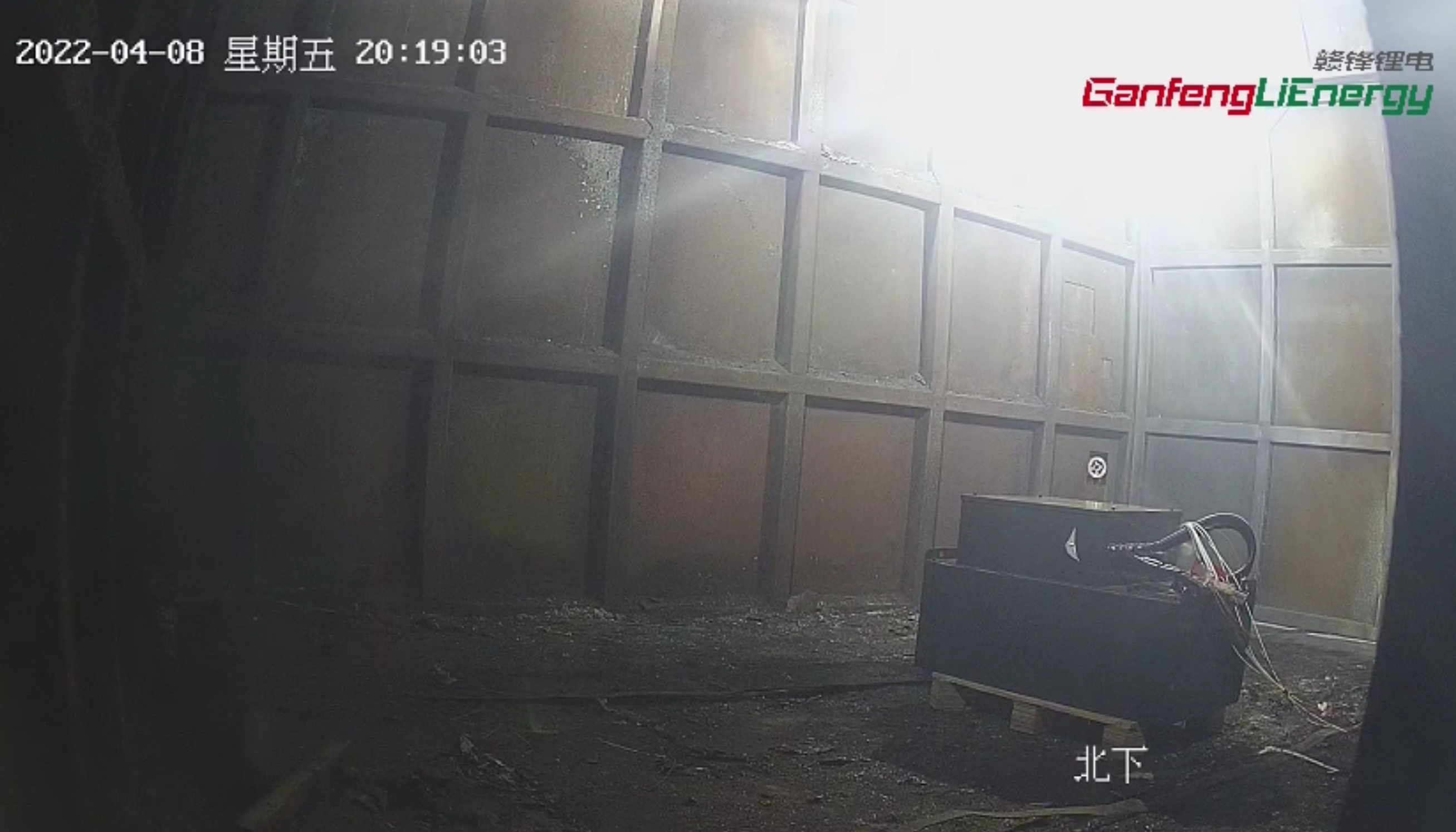 Ganfeng Lithium Battery Passed the Thermal Runaway Test
Ganfeng Lithium Battery Passed the Thermal Runaway Test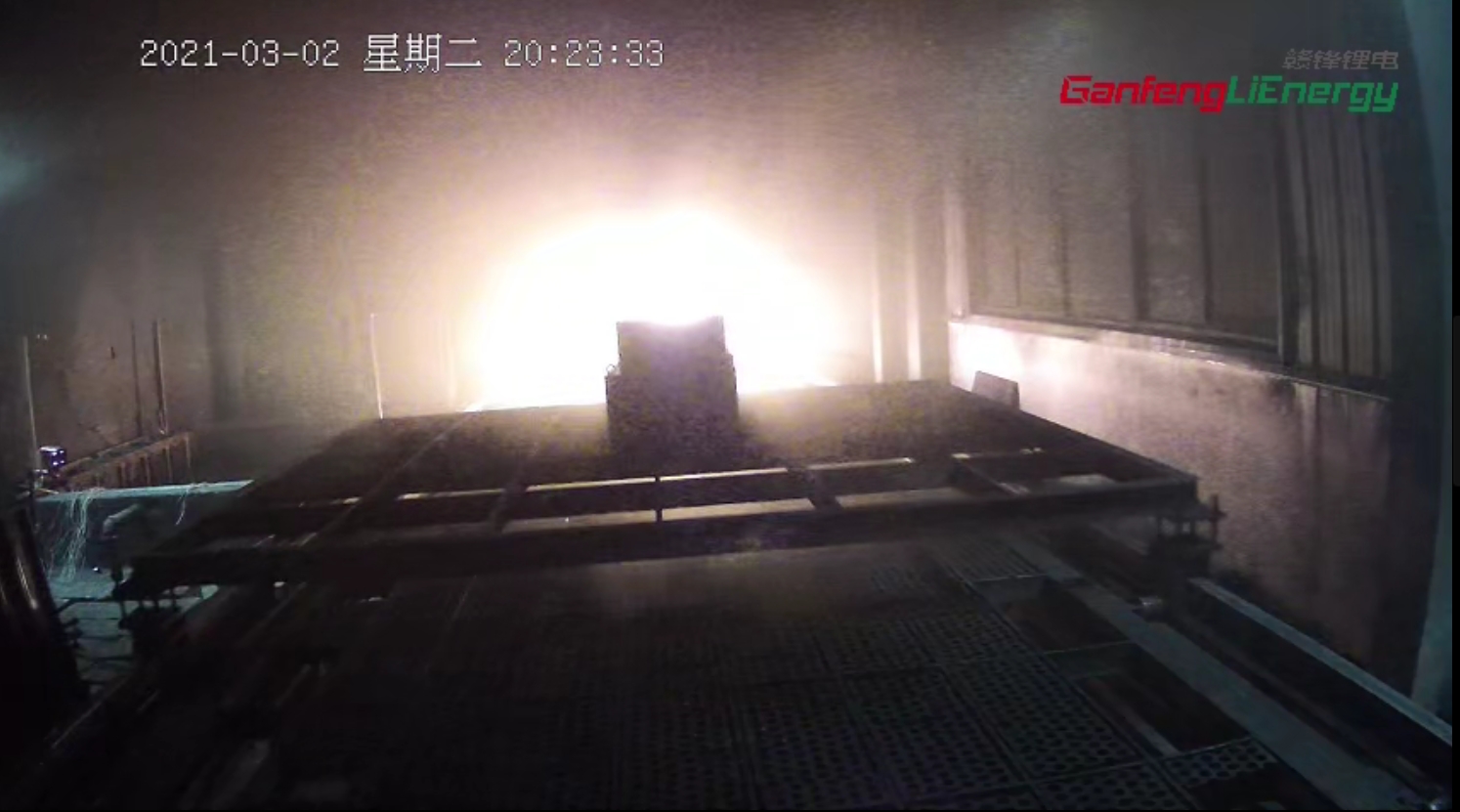 Ganfeng Lithium Battery Passed the Fire Test
Ganfeng Lithium Battery Passed the Fire Test Why use lithium batteries instead of lead-acid batteries?
Why use lithium batteries instead of lead-acid batteries? Questions about Forklift Lithium Batteries
Questions about Forklift Lithium Batteries Ganfeng Lithium's Goulamina project's first phase crushing production line completed ...
Ganfeng Lithium's Goulamina project's first phase crushing production line completed ... GanfengLiEnergy Battery won the title of Top 10 Chinese Energy Storage ...
GanfengLiEnergy Battery won the title of Top 10 Chinese Energy Storage ... Jiangsu Ganfeng's 100,000th Engineering Machinery Power Battery System Rolls Off ...
Jiangsu Ganfeng's 100,000th Engineering Machinery Power Battery System Rolls Off ... GanFengLiEnergy Showcases Multiple Innovative Energy Storage Products at WBE2024
GanFengLiEnergy Showcases Multiple Innovative Energy Storage Products at WBE2024